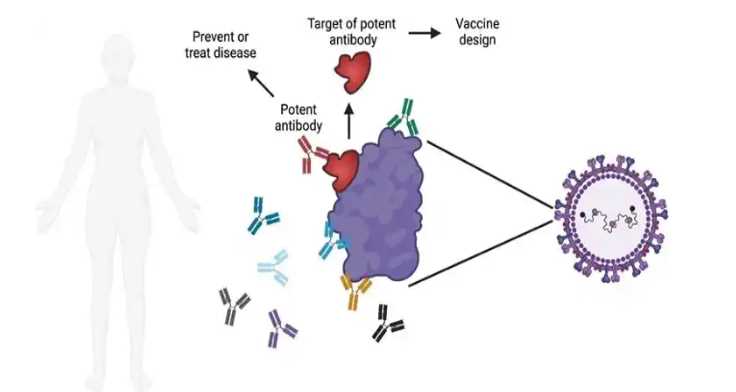
We have body soldiers who help fight different substances that could lead to various kinds of illness in the body. Thanks to the massive production of antibodies, which is one of the ways the body’s immune system helps wage war against foreign substances. In a world with growing technology, it is amazing that researchers can come up with antibodies that can specifically target some antigen, such as the type of antigen on cancer cells. Moreover, researchers can design different antibody copies in the laboratory. These antibodies are referred to as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs or Moabs).
What are monoclonal antibodies?
There’s a specific protein type produced in the laboratory that can bind to some targets in the human body. These include antigens on the cancer cell’s surface. Many kinds of monoclonal antibodies exist, such as the caspase one antibody. However, each monoclonal antibody is designed to stick to just an antigen. Monoclonal antibodies are useful in treating and diagnosing varieties of diseases such as certain cancer types. To get drugs, toxins, and radioactive substances into the cancer cells, this type of mAbs is useful.
Monoclonal antibodies refer to a class of medicines playing a major role in transforming how we prevent and treat diseases such as cancer, childhood viral infections, and immune system diseases. It is, however, important not to confuse mAbs as chemical compounds, just as most drugs. mAbs are naturally produced antibodies; they are proteins produced by the body for self-defense against certain diseases. It is pertinent to know that mAbs can be lab-created and massively produced in factories. As a result, some people refer to them as “designer antibodies” since they are tailor-made to treat diseases.
How mAbs work
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system, remaining major ways the body resists diseases. Just as antibodies work, the same way works mAbs by binding to a certain target. For instance, they make bacteria, viruses, or cancerous cells harmless by restricting their actions or flagging them as strangers, allowing other immune system parts to clear the strangers off.
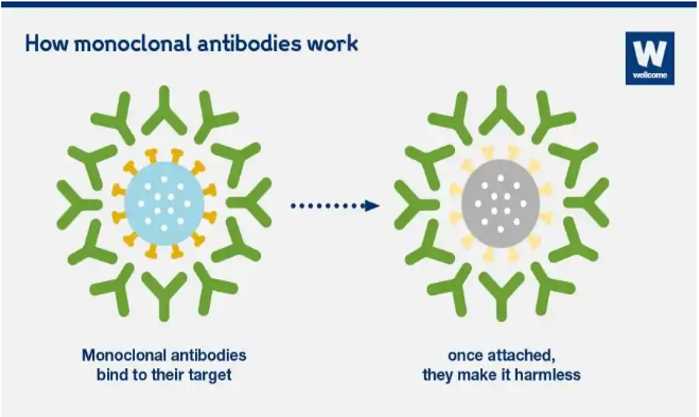
Can monoclonal antibodies treat Covid-19?
For more than three decades, mAbs have transformed how we treat various diseases. They have proved to be very powerful and effective, better tolerated, and difficult to deliver than other treatments. Researchers are convinced that mAbs can serve as prevention and treatment of infections that surface at an early stage, including early treatment of COVID-19. However, if mAbs would not treat COVID-19, they have loads of advantages to offer, such as the following:
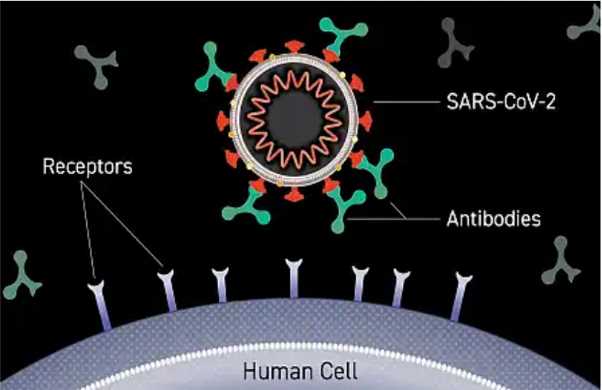
- Monoclonal antibodies can specifically target the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This is because their origination is from the survivor’s blood of COVID-19. As a result, they have more potential effectiveness compared to other drugs.
- Monoclonal antibodies can rapidly isolate or be manufactured. It can be surprising that since the pandemic broke out, over 70 mAbs products for the pandemic are currently under development process.
- Monoclonal antibodies can rapidly protect an individual from being infected. Once administered, it goes directly into the bloodstream immediately, providing the required protection for a couple of weeks or months. On the other hand, it may take weeks to see the effectiveness of vaccines. However, its protection is usually in the long term. This is why researchers believe that mAbs could complement vaccines to help contain COVID-19.
- Finally, mAbs have the potential to treat people infected with COVID-19 and prevent infection in people, ranging from children to older people, including immunocompromised persons who are unable to get vaccinated or people who find the vaccine to be ineffective.
The production of mAbs
The production of mAbs such as GAPDH antibodies may be expensive and complex. To start with, scientists extract the relevant antibodies from the human blood. After the extraction process, they ensure to reciprocate them, producing them in larger quantities. Most mAbs are produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells, typically grown in large bioreactors for about two weeks or more. They further purify the results and package them for easy administration. However, expensive materials and time are dedicated to the production process. According to some people’s estimation, it is believed that the production cost of a gram of marketed mAbs such as EZH2 antibody is between $95 and $200. However, these costs exclude both research and development costs, packaging, delivery, and even the cost to administer it. For startup companies, the costs go much higher. Manufacturers are concerned about finding a solution to the outrageous cost of production.
Conclusion
Monoclonal antibodies offer amazing benefits to the body and have proved to be capable of fighting loads of diseases. However, we have seen their benefits towards the treatment of COVID-19. Even if they don’t seem to cure COVID-19, they are great for managing it while simultaneously fighting other underlying diseases.